Soluciones
eficientes para sistemas de riego
Irrigación para el futuro sostenible del agua.
Gestiriego
Desde 1985 aportando soluciones globales para la agricultura de alto rendimiento. El GRUPO GESTIRIEGO está formado por una amplia red internacional de delegaciones y distribuidoras extendidas por todo el mundo, con sede central en España. Nuestra prioridad es ofrecer al agricultor el mayor rendimiento de sus cultivos con sistemas de riego de máxima eficiencia, contribuyendo a la sostenibilidad del medioambiente.
Sistemas de riego
Soluciones de riego agrícola profesional
Innovación, desarrollo y fabricación de los sistemas de riego más avanzados
Nuestra oferta se compone de 14 familias de productos de riego agrícola que cubren todas las necesidades de un sistema de riego por goteo agrícola.
Contamos con todos los elementos necesarios para crear “El Camino del Agua”, haciendo un completo catálogo de más de 2.000 referencias en materiales de riego profesional.
Nuestras sedes
Península y Baleares, Canarias, México y Chile.
Gestiriego por el mundo.
01.
Península y Baleares
Nuestra sede principal se encuentra en España, desde 1985 comprometidos con una agricultura eficiente y sostenible, apostando por la innovación y la excelencia en todos nuestros sistema de riego. Apostando por la internacionalización y creando filiales por puntos estratégicos del planeta.
02.
Islas Canarias
En 2003 abrimos nuestra primera sede en Tenerife (Islas Canarias), un almacén de 750 metros cuadrados. En 2022 inauguramos nuestra segunda sede en Tenerife, tercera en el archipiélago, con otros 1.000 m2, cubriendo la demanda total, de norte a sur de la isla.
03.
México
04.
Chile
En 2001 abrimos nuestra primera sede en Chile con un almacén de distribución estratégica para dar servicio regular. En 2008, trasladamos nuestras instalaciones junto al aeropuerto de Santiago de Chile, ocupando una nave de 5.000 m2 para asegurar el stock demandado.
Sistemas de Riego destacados
Productos destacados
Los mejores materiales de riego.
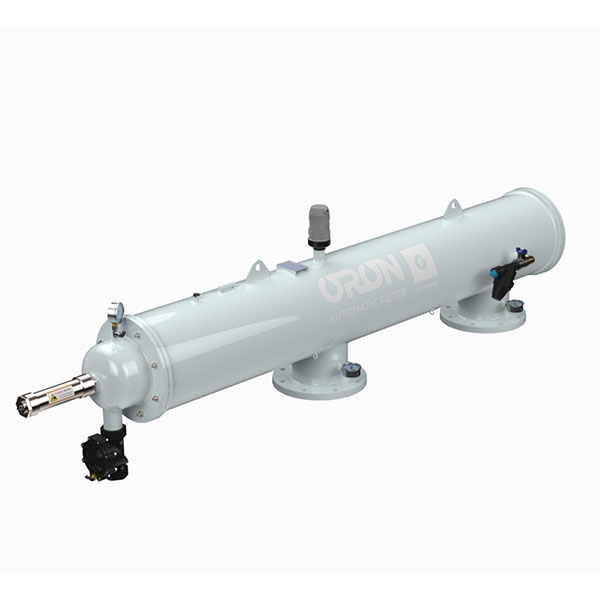

Filtros de riego Oron
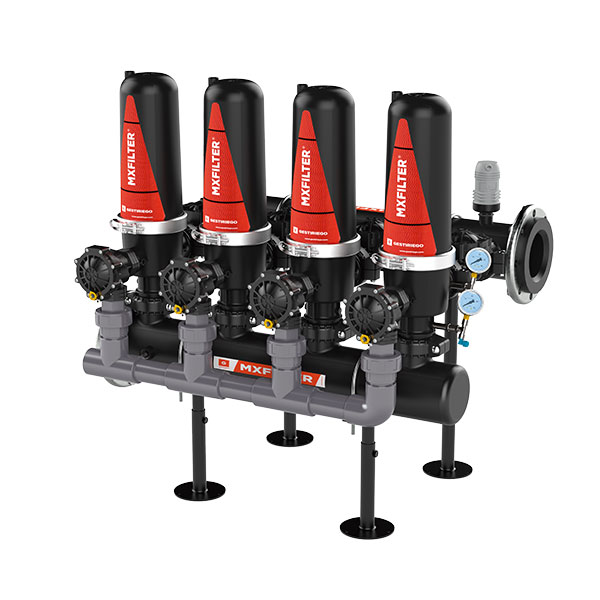

Cabezales automáticos 3 vías
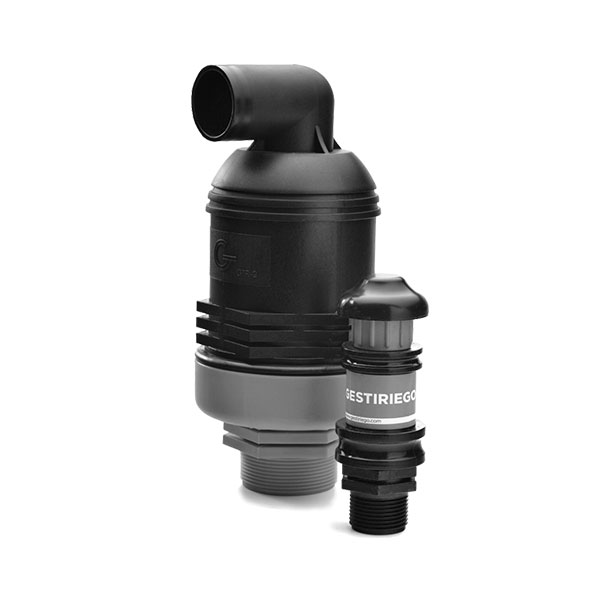

Ventosas GTR doble efecto
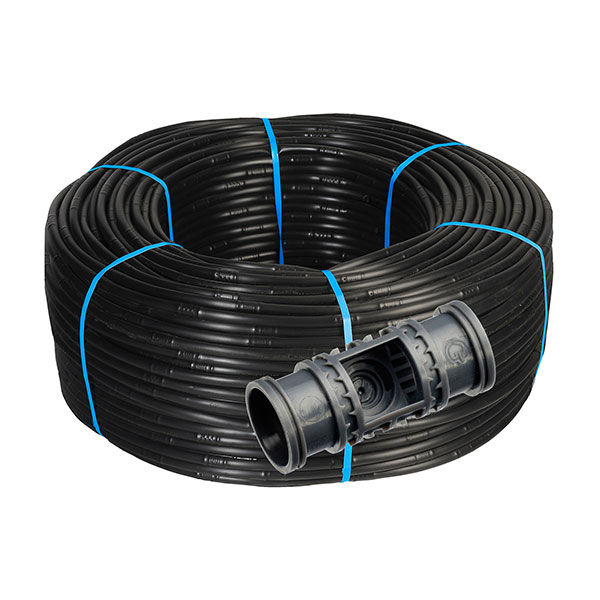

Starcomp Neo Ø16 / Pared 1 mm
Categorías
Productos para un riego eficiente
Materiales de riego profesional
Filtros
de riego
Los mejores y más avanzados sistemas de filtrado de precisión para riego.

Fertirrigación
Sistemas de fertirrigación para asegurar la eficiencia y la sostenibilidad de cultivos.

Riegos
automáticos

Tuberías
polietileno
Accesorios
tuberías
Riego
por goteo
Accesorios
riego por goteo
Herramientas
riego
Fichas técnicas Gestiriego
Todo lo que necesitas está en nuestro catálogo.
Contamos con una amplia gama de productos y sistemas de riego accesibles para la agricultura y la conducción del agua. Descarga nuestro catálogo o accede a nuestras fichas técnicas para ampliar información.


Calidad, eficiencia y sostenibilidad.
Tuberías de polietileno para sistemas de riego.
Carsystem es la marca bajo la que Gestiriego fabrica tuberías de polietileno para sistemas de riego y conducciones de agua. 30 años de experiencia de fabricación, garantizan nuestra excelente calidad y la anticipación a las necesidades del cliente.
Dentro de nuestra línea agrícola, somos especialistas en la fabricación de tuberías de microirrigación y de presión. Con el objetivo de cumplir los más alto estándares de calidad, contamos con la certificación AENOR de producto para nuestras tuberías de P100 y P40 para uso alimentario.
Especialistas en riego por goteo
Si eres agricultor y buscas un sistema de riego eficiente y preciso para tus cultivos, el riego por goteo es la opción ideal. Y si estás buscando una empresa líder en el diseño, instalación y mantenimiento de sistemas de riego por goteo en España, Gestiriego es la elección perfecta.
En Gestiriego contamos con una amplia experiencia y un equipo de profesionales altamente cualificados que te ayudarán a obtener el máximo rendimiento de tus cultivos.
Ofrecemos un diseño personalizado adaptado a tus necesidades y características, instalaciones eficientes y seguras, sistemas de riego de alta calidad y tecnología avanzada, mantenimiento preventivo y correctivo y un asesoramiento técnico y soporte al cliente de alta calidad.
El riego por goteo puede ser utilizado en una amplia variedad de cultivos, desde hortalizas, frutales, cultivos ornamentales, hasta plantaciones forestales y viñedos. Este método de riego permite una aplicación precisa del agua, reduciendo al mínimo la pérdida de agua y optimizando el uso de los recursos hídricos.
El riego por goteo puede mejorar la calidad y cantidad de la cosecha, reducir el consumo de energía y fertilizantes, y disminuir el impacto ambiental.
En Gestiriego entendemos la importancia del riego por goteo para el éxito de tus cultivos y estamos comprometidos a ofrecerte los mejores sistemas de riego y el mejor servicio al cliente. Si estás buscando un sistema de riego por goteo eficiente y de alta calidad, no dudes en contactarnos. Estamos listos para ayudarte a mejorar la rentabilidad y sostenibilidad de tus cultivos.
Noticias
Te mantenemos informado
Noticias sobre el sector y Gestiriego.
En nuestro apartado de noticias encontrarás todas las novedades relacionadas con la agricultura, sistemas de riego para los diferentes tipos de cultivos, artículos informativos, los productos más destacados del momento, etc.
Así como todo lo referente a nuestra empresa de riego agrícola y todas sus filiales; noticias relevantes, eventos, ferias, innovación de productos, etc.
Contáctanos
¿Tienes alguna duda o quieres solicitarnos presupuesto?
Contacta con nosotros sin compromiso. Intentaremos responder lo antes posible.